|
Download Members: $0.00 Non‑Members: $75.00 |
Buy Now |
Publication Details
| Published Date: | |
|---|---|
| Download Format: | |
| Citation: | Farid Javidpour, Edward Morse |
Abstract
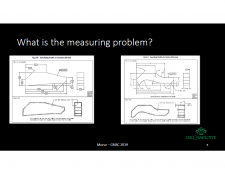
One of the major differences between tactile and optical profile scanning methods is the sampled point density. Not only do optical methods collect many more points, the point spacing (which is almost uniform in tactile measurement) can be highly variable in optical scanning. This non-uniform density in the measured point cloud results in variations in the fitting to nominal geometry, especially when the Least Squares method is used. To analyze the combined effect of point density and fitting algorithm, a simple Least Squares (LS) and a Weighted Least Squares (WLS) algorithm were each applied to measurement data obtained from tactile and optical scans of 2D profiles having irregular shapes. To evaluate the influence of the weighting strategies, a profile comparison metric was devised that utilizes a convolution averaging filter on the measured profile data. Using this filtering technique, the differences in the mean local deviations between the two algorithms was evaluated. In the experiments that were performed on the two profiles, the point density variation caused a minimum change of about 80 micrometers when fitting the optical data and 4 micrometers when fitting the tactile data.





